Explain the Different Types of Unemployment Discussed in the Text
The book does not even acknowledge this type of unemployment. Three particular types of unemployment stand out as most important frictional unemployment structural unemployment and cyclically unemployment Some people who are not working are simply between jobs.
Types Of Unemployment Economics Help
Cyclical frictional and structural.

. Begin by distinguishing between the three types of unemployment discussed in this chapterfrictional unemployment structural unemployment and cyclical unemployment. There are 4 types of unemployment. Structural cyclical and frictional.
The deviation of unemployment from its natural rate What externalities are created by unemployment insurance minimum-wage laws and unions. There are three main types of unemployment. Cyclical frictional and structural.
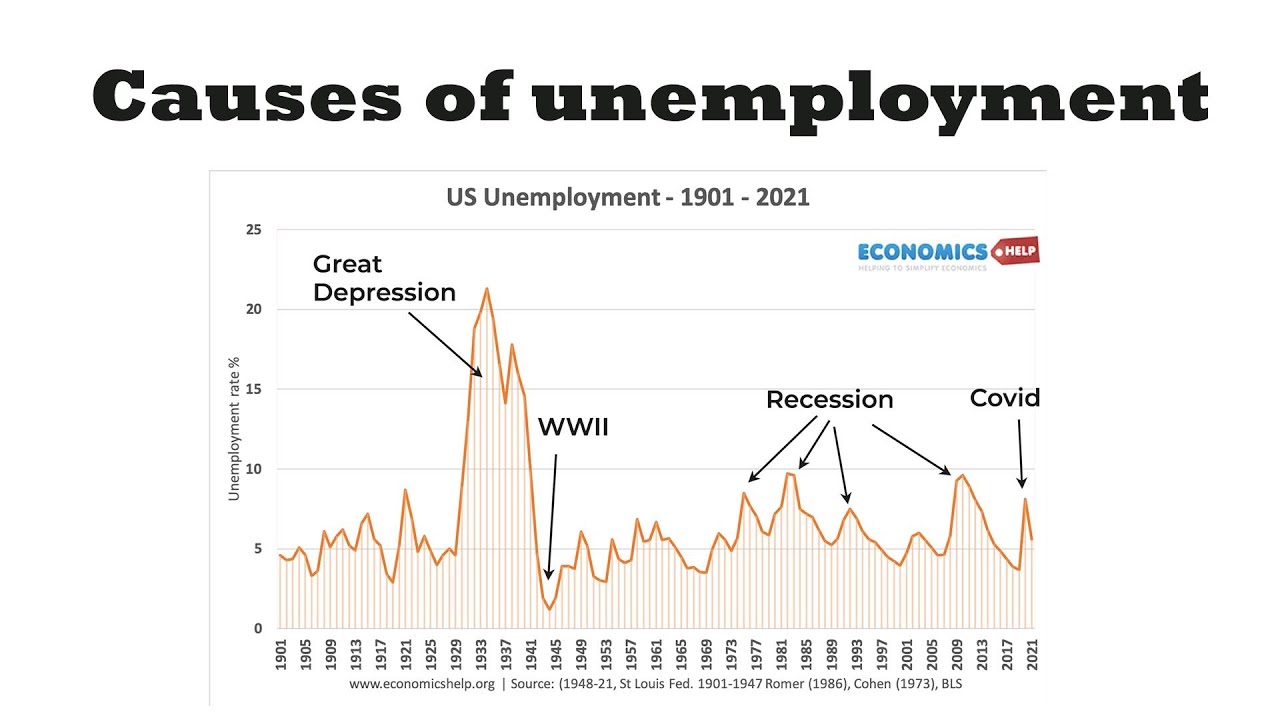
This form of unemployment is usually short-lived in nature. Figure 55 The Natural Level of Employment applies the demand and supply model to the labor market. Each source of unemployment has quite different implications not only for the workers it affects but also for public policy.
Differentiate between how the unemployment rate labor force participation rate are. Use a simplified numerical example with two different years to show your understanding 2. It occurs during a recession.
Economists distinguish between various overlapping types of and theories of unemployment including cyclical or Keynesian unemployment frictional unemployment structural unemployment and classical unemployment. Certain industries and types of occupations decline and others grow. Meanwhile cyclical unemployment is caused by cyclical trends in the business cycle.
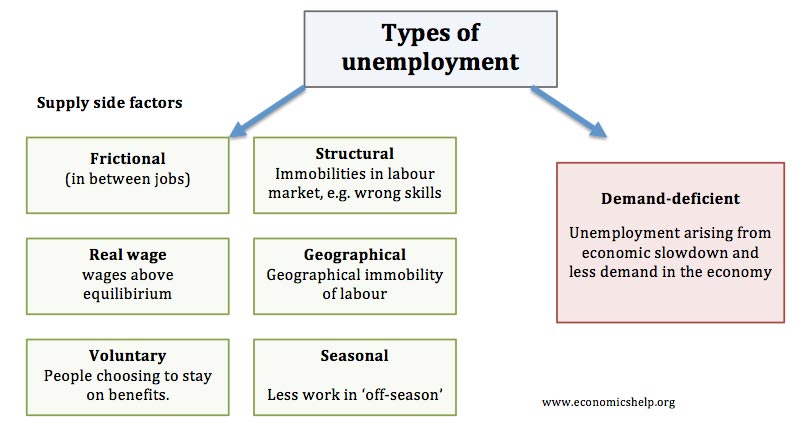
Types of Unemployment. There are basically four types of unemployment. As industries shrink they need fewer workers and they eliminate positions permanently.
Todays economists point to two main types of unemployment. They are not actively searching for a job but instead just waiting to begin their next job. Structural Unemployment Individuals are unemployed due to a lack in skills that modern industries need change in technology.
Frictional unemployment is the result of voluntary employment transitions within. The price of labor is taken as the real wage which is the. Frictional Unemployment When an individual is unemployed because they are looking for a new job.
Define and give examples of the three types or categories of unemployment discussed in class. Cyclical structural and frictional. Disguised unemployment is generally traced in unorganised sectors or the agricultural sectors.
This unemployment that rises and falls over time. Workers may find themselves unemployed for different reasons. This article summarizes nine types of unemployment.
There are three main types of unemployment. Frictionally unemployed people are in between jobs or are students who just completed school and are looking for a job. Seasonal Unemployment As its name suggest seasonal unemployment happens during certain seasons in a year when demand for labor declines during the off-seasons.
The Four Types of Unemployment Four commonly distinguished forms of unemployment are. Cyclical unemployment is the unemployment associated with the ups and downs of the business cycle. Seasonal frictional cyclical and the most problematic structural unemployment.
This is a type of unemployment where people employed are more than actually needed. Structural cyclical and frictional unemployment. Cyclical Unemployment When individuals lose jobs due to a fall in aggregate demand often during an economic recession.
Three types of unemployment. 2 Explain how the reported unemployment percent is calculated. Structural unemployment arises from a mismatch between the skills offered by workers and the skills demanded by employers.
Economists primarily focus on three types of unemployment. This unemployment arises when there is a mismatch between the workers skills and. Explain the different types of unemployment discussed in the text give an example of each in your discussion.
People who lose jobs in these. This is unemployment that happens at the same time every yea r due to seasonality. In addition when discussing the concept of structural unemployment use.
1 demand deficient 2 frictional 3 structural and 4 voluntary unemployment. Demand deficit unemployment is the biggest cause of unemployment that typically happens during a recession. There are three main types of unemployment.
1 Cyclical unemployment is unfortunately the most familiar. Structural unemployment results from changes in the structure of the economy. Cyclical unemployment occurs because of the ups and downs of the economy over time.
Explain the difference between nominal and real GDP. 3 Explain how the reported unemployment percent is misleading and how politicians have used it to their advantage. Use a specific real-world example of each to make these concepts less abstract to the students.
During recessions cyclical unemployment increases and drives up the unemployment rate. Reduces hardship for unemployed makes people reject unappealing jobs less like to care about job security. The textbook distinguishes between four types of unemployment i.
This may be the result of being hired elsewhere or simply relocating. The types of unemployment are discussed below. The second twostructural and frictionalmake up the natural unemployment rate.
The state of being without any work yet looking for work is called unemployment. They differentiate between at least three types of unemployment.
Types Of Unemployment Economics Help

Major Factors That Cause Different Types Of Unemployment Education Major Business And Economics Business Journalism

Discouraged Workers Find A Job Looking For A Job Discouraged
Comments
Post a Comment